XSL, or Extensible Stylesheet Language, is a language used for expressing style sheets. It is primarily used for transforming and rendering XML documents. You can think of XSL as a way to define how the information in your XML files should be displayed, whether it be in HTML, text, or other formats.
How does XSL relate to XML?
XSL works in tandem with XML by providing a means to style and present the data contained within XML documents. While XML is primarily concerned with data structure and storage, XSL ensures that the data is displayed in a meaningful and organized manner.
What components does XSL include?
XSL consists of three main components:
- XSLT (Transformations),
2. XPath (Navigating XML Nodes),
3. XSL-FO (Formatting Objects).
You use these together to navigate, transform, and format XML documents effectively.
Can I use XSL to convert XML to HTML?
Yes, XSL can be used to convert XML documents into HTML. By doing so, you can present your XML data in a web browser as a web page. This is typically achieved using XSLT, a sublanguage of XSL, which allows you to transform XML data into different formats.
Is XSL similar to CSS?
While both XSL and CSS are used to style document content, they serve different purposes. XSL is more powerful and complex, designed specifically for XML documents, and capable of transforming document structure. CSS, on the other hand, is used mainly for styling HTML documents and cannot transform document content.
How do I apply XSLT to an XML document?
To apply XSLT to an XML document, you need an XSLT processor. The processor reads both the XML document and the XSLT stylesheet, then transforms the XML data according to the rules set in the XSLT. The output can be HTML, text, or another XML document.
Does XSLT support conditional logic?
Yes, XSLT supports conditional logic using “ and “ elements. These allow you to specify conditions under which certain pieces of the XML should be processed, similar to `if-else` statements in programming.
Can I include loops in my XSL?
Absolutely, XSL includes looping capabilities with the “ element. This allows you to iterate over a set of XML nodes and apply transformations to each node, which is useful when you need to process repeating elements.
What is the purpose of XPath in XSL?
XPath is used within XSL to navigate through elements and attributes in an XML document. It allows you to select specific nodes, attribute values, or entire node sets based on defined criteria, making it foundational for effective XML document transformation.
Can XSL handle different data types?
XSL can handle several data types, such as strings, numbers, and boolean values. It offers various functions to manipulate these data types, enabling you to perform operations like string concatenation, arithmetic computations, and logical comparisons.
How do namespaces work in XSL?
Namespaces in XSL help avoid name conflicts by distinguishing between elements and attributes that may have the same name but belong to different XML vocabularies. You can declare and use namespaces in your XSL documents to ensure clarity and prevent overlap.
Does XSL support templates?
Yes, XSL supports templates. You can define multiple templates in an XSLT stylesheet to match and transform different parts of your XML document. Templates are reusable and help in applying consistent transformations across your XML data.
What are XSL formatting objects?
XSL-FO, or Formatting Objects, is a subset of XSL intended for describing the layout and formatting of XML documents for print or pagination. Unlike XSLT, which focuses on transforming XML into other formats, XSL-FO handles the detailed styling and appearance of the final output.
Can I use XSL for data extraction?
Yes, you can use XSL, particularly with XSLT and XPath, to extract data from XML documents. By defining templates and specifying XPath expressions, you can filter and select relevant data for further use or transformation.
Can I embed scripts in XSL?
Yes, you can embed scripts in XSLT using “ or extensions, though this is less common and can depend on the XSLT processor you are using. These scripts can be used to perform more complex operations that may not be achievable with standard XSLT.
What is the role of the “ element?
The “ element in XSLT is used to process and transform child elements of the current node. Instead of manually specifying the transformation for each child element, this element allows you to apply predefined templates, enhancing modularity and reusability of the transformation rules.
Can I use XSLT to sort XML data?
Yes, XSLT can be used to sort XML data. By leveraging the “ element within an “ or “ element, you can define sorting criteria based on the values of specific nodes or attributes. This allows you to control the order in which elements appear in the output.
How does “ differ from “?
The “ and “ elements both allow you to incorporate external stylesheets into your XSLT document. The key difference is that “ gives precedence to the importing stylesheet’s templates, while “ treats all templates equally, potentially causing conflicts if template rules overlap.
What is the significance of the “ element?
The “ element in XSLT defines a lookup mechanism to improve the efficiency of XML document processing. By creating keys, you can quickly access specific nodes based on their values, which is particularly useful for large documents or complex transformations involving repeated element look-ups.
More on XSLT
XSL transformation is used to to transform XML data into either other XML formats, HTML, or text.
XSL uses XPath as its matching engine, which is another standard in the industry. XSL is, in its most basic form, a matching engine of XML patterns directed by XPath selectors. For more information on XPath, visit http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath.
XSL basics
XSL is written in XML format with use and support of namespaces. The style of writing XSL is by entering xsl:template elements that match a given criteria (an XML path, a condition for an XML path, etc.). The flow of code is directed by xsl:apply-templates elements placed within templates, in a parent-child manner. This is similar to the declarative XML processing where the xsl:template is equivalent to <#macro…> elements, while xsl:apply-templates is somewhat equivalent to <#recurse>. XSL is more powerful than the declarative model because it allows recursion in which the path selection is defined in a more specific way.
The XSL language supports xsl:for-each, xsl:choose and xsl:if as programmatic constructs. These constructs resemble the <#list>, <#if> and <#switch> directives. Note that XSL functionality are somewhat limited.
XSL processing
You use the xslt method for XSL processing. The xslt method receives two XML nodes, which you need to previously initialize with parsexml, and perhaps load. The first parameter is the node of the XML to be transformed. The second parameter is the node of the XSL transformation (which is, by definition, XML as well).
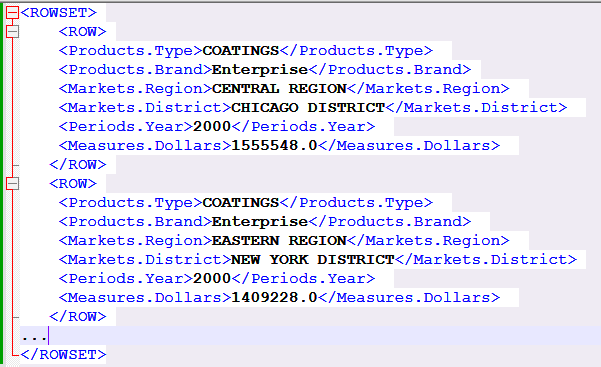
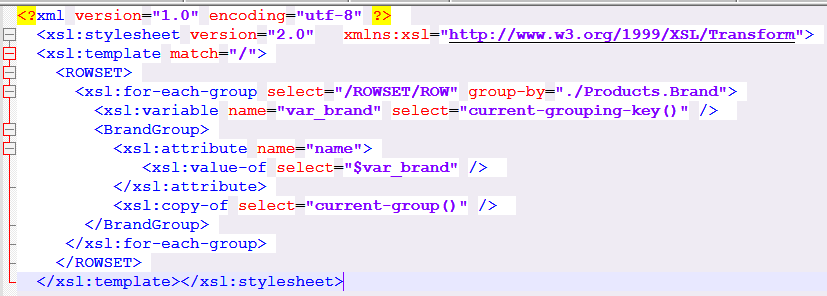
Split above xml data by a Field
how to use an XSLT preprocess file to create a grouping in the data that will enable the splitting of the data across multiple Excel sheets based on the grouping.
This example groups the sample data by the Products.Brand field.
This sample XSLT file groups the data according to <Products.Brand> and creates a high level element <BrandGroup> for each of those groups.
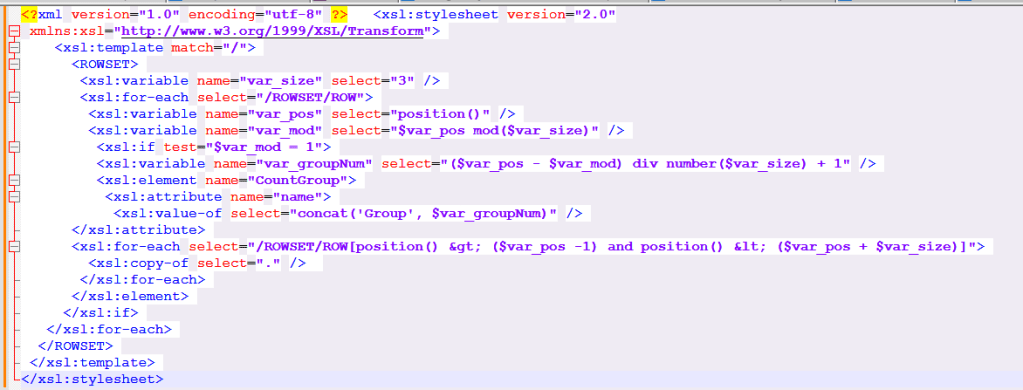
Split above xml data by Count of Rows
Group above XML data by the count of occurrences of /ROWSET/ROW, and then configure the Excel template to create a new sheet for each occurrence of the newly created group.
Create an XSLT file to create groups in the data according to a size specified in a variable.The following sample XSLT file groups the occurrences of /ROWSET/ROW according to the value of $var_size and creates a high level element <CountGroup> for each of those groups.